Fingernails
Fingernails:
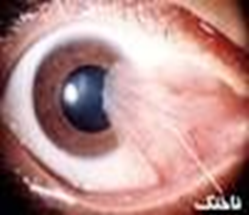
The pterygium is a triangular lesion that extends from the whites of the eyes (conjunctiva) to the black of the eye (cornea). This lesion is caused by the benign growth of connective tissue and conjunctival vessels.
The pterygium usually first develops as a whiteness on the conjunctiva, which gradually grows toward the cornea. Due to the large number of vessels, the pterygium is usually pink or red.
The pterygium sometimes becomes inflamed, causing burning, itching, and tears. Sometimes it grows so large that in the middle of the cornea, in addition, even smaller pterygium can cause astigmatism and blurred vision by deforming the cornea.
Prevention:
The sun’s UV rays are effective in creating pterygium, so it is recommended that people who live in sunny areas and are exposed to the sun for a long time wear a brimmed hat and sunglasses. Also, strong winds and dust may be effective in causing pterygium by irritating the eyes.
In people with pterygium, water entering the eyes (when washing hands and face or taking a bath) irritates the eyes and causes irritation and redness of the eyes. Therefore, these people should be careful not to get water in their eyes as much as possible.
treatment :
If the pterygium is small and does not have an unpleasant appearance and does not cause redness and irritation of the eyes, no special treatment is needed. However, if the pterygium sometimes becomes inflamed and causes eye irritation, frequent use of artificial tear drops will relieve the symptoms. In cases where the pterygium is severely inflamed, a course of treatment with steroid drops or other anti-inflammatory drops can be performed with the opinion of an ophthalmologist.
Larger pterygiums that are important in terms of appearance or have caused blurred vision due to astigmatism can be removed with pterygium surgery. However, if the pterygium is removed simply, it is more likely to recur, especially in young people and people who They have inflamed nails. Recurrence is seen in half of the cases. In these people, in addition to removing the pterygium, it is better to use complementary methods such as:
Conjunctival transplantation or the use of specific mitomycin drugs during surgery. In very large pterygiums that involve the middle of the cornea, it may be necessary to use a layered corneal transplant in addition to the above procedures to correct the corneal problem.
It should be noted that some ocular tumors may be mistaken for pterygium at first, so in cases where the pterygium grows very rapidly or recurs frequently, we should see an ophthalmologist.
Postoperative nursing care:Do not open the dressings on the eyes after the operation.
The first dressing should be opened by a doctor.
It is normal to have some pain and runny nose and nose.
Acetaminophen can be used to reduce pain.
After the doctor opens the dressing, follow the recommendations regarding eye drops and the time when the drops should be poured.
If several different drops should be instilled in the eye at a certain hour, the minimum distance between each drop and the next drop should be 5 minutes.
Avoid rubbing the eyes.
Remove the eye protection only when pouring eye drops and put it back on the eye after dropping the drops.
See your doctor at regular appointments for your next checkup
